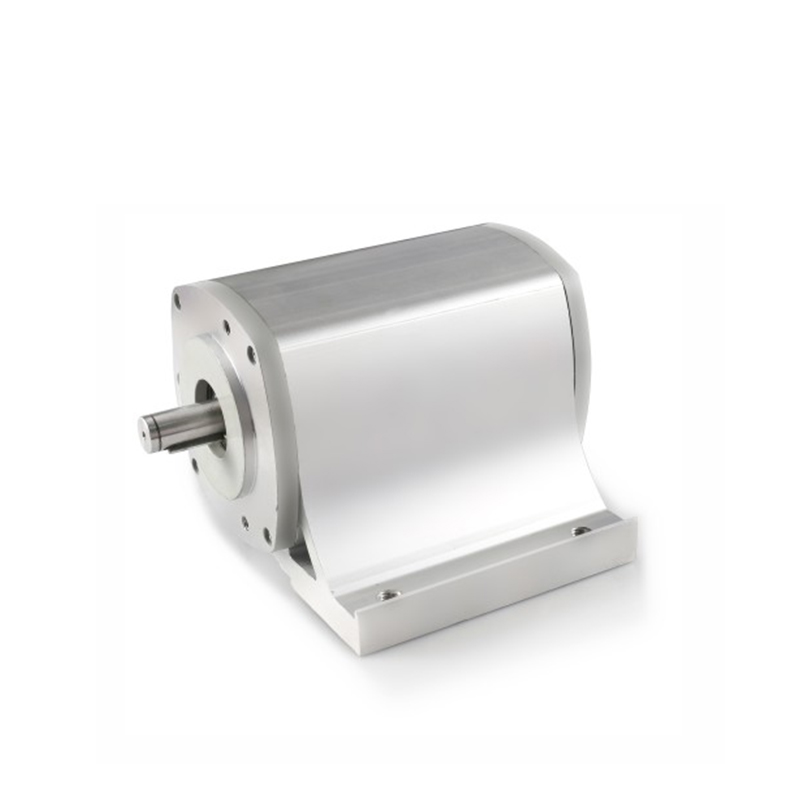
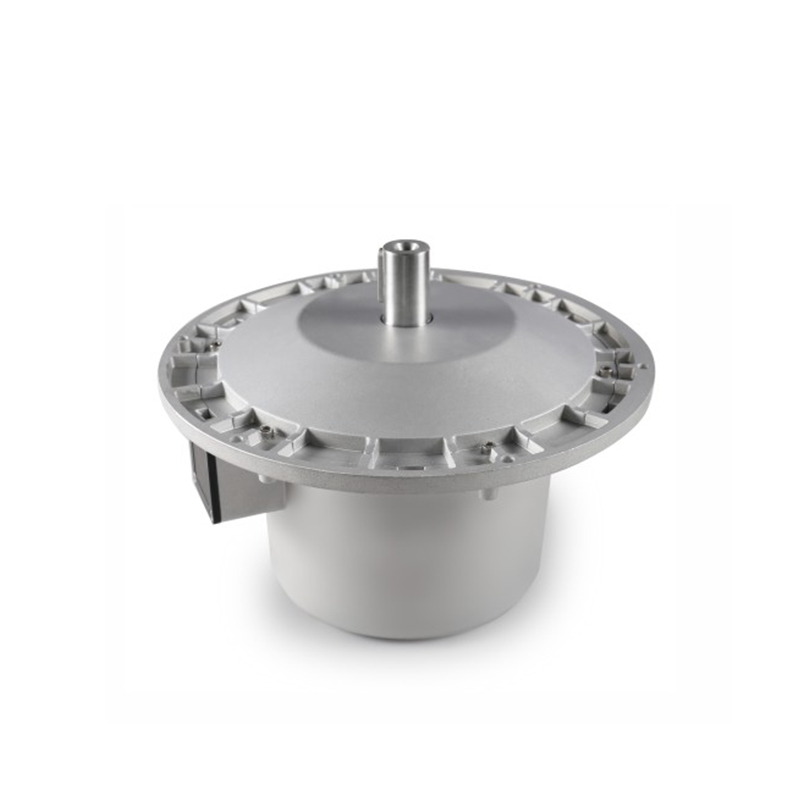
What Is a DC Actuator and How Does It Work?
In many fields such as automation control, robotics, medical equipment, smart furniture and industrial equipment, the actuator is a key component. It is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical motion to achieve actions such as pushing, pulling, lifting, and rotating. A DC actuator is an electric actuator driven by a DC power supply. It is widely used in various linear and rotary motion systems due to its simple structure, convenient control and sensitive response.
1. What is a DC actuator?
A DC actuator, full name Direct Current Actuator, is an electric device driven by a DC power supply. Its main function is to convert electrical energy into controllable linear (straight) or rotary motion to perform actions such as opening, closing, pushing, pulling, and lifting.
It is usually composed of motors, reduction mechanisms, screws (or gears), limit switches, controllers and other components, and can complete automation or remote operations according to external control signals.
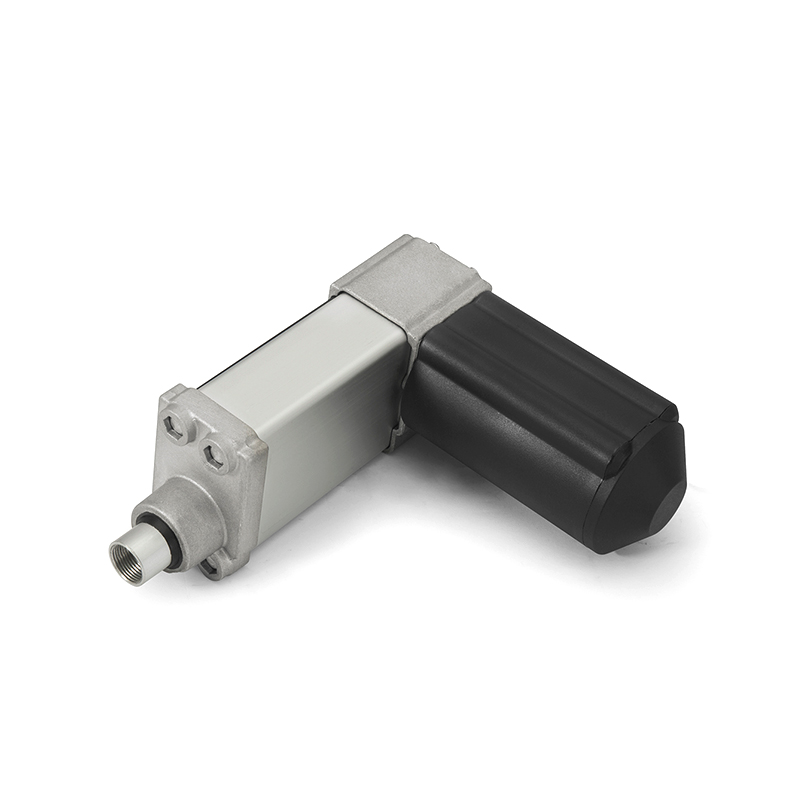

2. Main types of DC actuators
DC actuators can be divided into the following types according to the output motion form and structure:
1. DC linear actuator (DC Linear Actuator)
The output is linear push-pull motion
Commonly used in lifting systems, door and window opening devices, bed adjustment, solar trackers, etc.
2. DC rotary actuator (DC Rotary Actuator)
The output is rotary motion
Applied to valve control, electric door locks, electric regulators, etc.
3. Miniature DC actuator (Miniature Actuator)
Small size, low voltage (such as 12V, 24V), suitable for use in small spaces
Commonly used in robots, medical equipment, and smart electronic products
3. Core components and working principles of DC actuators
1. Motor (Motor)
The core driving source of DC actuators is a DC motor, generally a brushed DC motor or a brushless DC motor.
Brushed motors have a simple structure and low cost
Brushless motors have high efficiency, long life and low noise
2. Gearbox
The high-speed rotation of the motor is reduced through gears to increase torque and make the output more controllable and stable.
3. Transmission mechanism
Commonly used are screws, ball screws or gear racks, which convert rotational motion into linear motion or control angle output.
4. Limit switch
Used to set the end point of motion to prevent overshoot from causing damage to the equipment.
5. Control circuit or module
Including relays, PWM speed regulation, position feedback devices (such as potentiometers or Hall sensors), used to achieve speed control, stroke control, position feedback and other functions.
4. Working principle of DC actuator
The working process of DC actuator is as follows:
Power on and start: The control system powers on the DC motor to drive the actuator to operate;
Deceleration and transmission: The motor rotates at high speed, and after gear deceleration, it drives the screw or gear mechanism;
Achieve motion output:
If it is a linear actuator: The screw rotates to push the push rod to move forward and backward in a straight line;
If it is a rotary actuator: The output shaft rotates a certain angle or rotates continuously;
Limit protection: After the movement reaches the set end point, the limit switch or controller is powered off and stops automatically;
Reverse operation: Changing the direction of the current can achieve reverse action (such as retraction).
Precise speed and stroke control can also be achieved through PWM speed control, position sensor feedback and other functions.
5. Advantages of DC actuators
Simple control: only positive and negative power supplies are needed to control the direction, and it is easy to integrate into various systems
Fast response: sensitive starting and braking, suitable for dynamic load control
Low voltage drive: commonly used 12V/24V power supply, suitable for mobile or battery-powered devices
Compact structure: small size, suitable for equipment with limited space
Low noise, low maintenance: especially brushless models, stable operation and long life
6. How to choose a suitable DC actuator?
When selecting, the following parameters should be considered:
Stroke Length: The distance the actuator pushes, commonly available in 50mm~500mm;
Load Capacity: The unit is N or kg, and the maximum load value needs to be considered;
Speed: The unit is mm/s, and the speed is usually inversely proportional to the load;
Voltage: Commonly 12V, 24V, and there are also 36V/48V customized models;
Installation method: Pay attention to whether the installation point size and connection method match;
Protection level: Whether it has waterproof and dustproof functions (such as IP65);
Control method: Whether position feedback, remote control, PLC control, limit adjustment, etc. are required;
Use environment: temperature range, whether it is used outdoors or in corrosive environments, etc.
As an important drive component in modern automation systems, DC actuators play a key role in many fields such as home, industry, medical care, and agriculture with their flexibility, efficiency, and easy control. With the development of intelligent control technology, DC actuators are also evolving, with higher precision, stronger adaptability and smarter feedback systems.
If you are considering introducing electric push rods or small automatic drive equipment, understanding the basic principles and application characteristics of DC actuators will help you select more accurately and improve the overall performance and stability of the system.
-
Feedback
Hotline:0086-15869193920
Time:0:00 - 24:00


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch italiano
italiano 中文简体
中文简体