Author: Admin Date: 2024-03-27
What are the key components of a brushless geared motor system, and how do they work together?
A brushless geared motor system comprises several key components that work together to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion efficiently. Here are the main components and their functions:
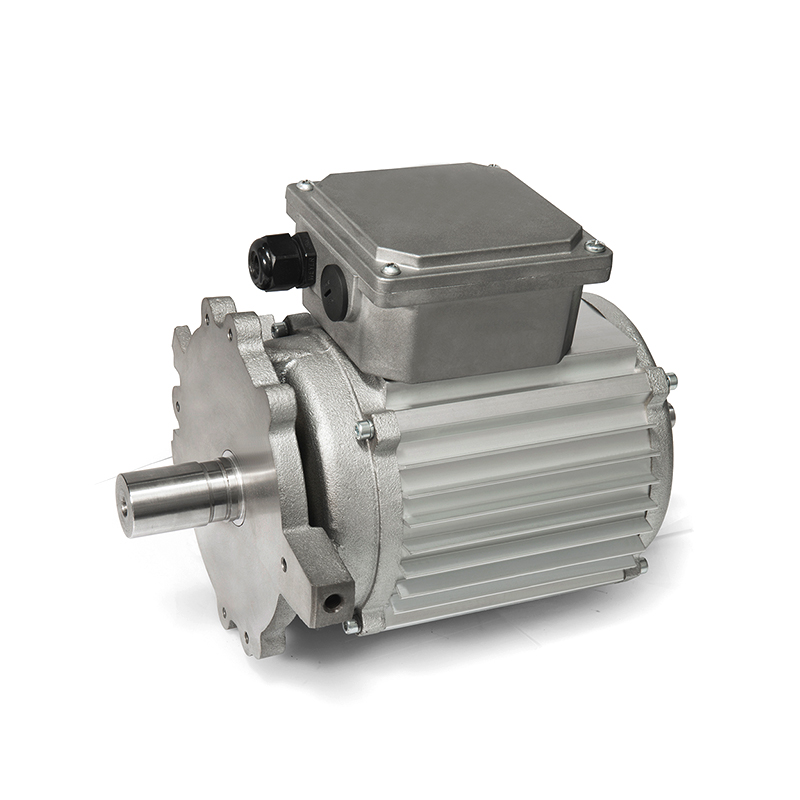
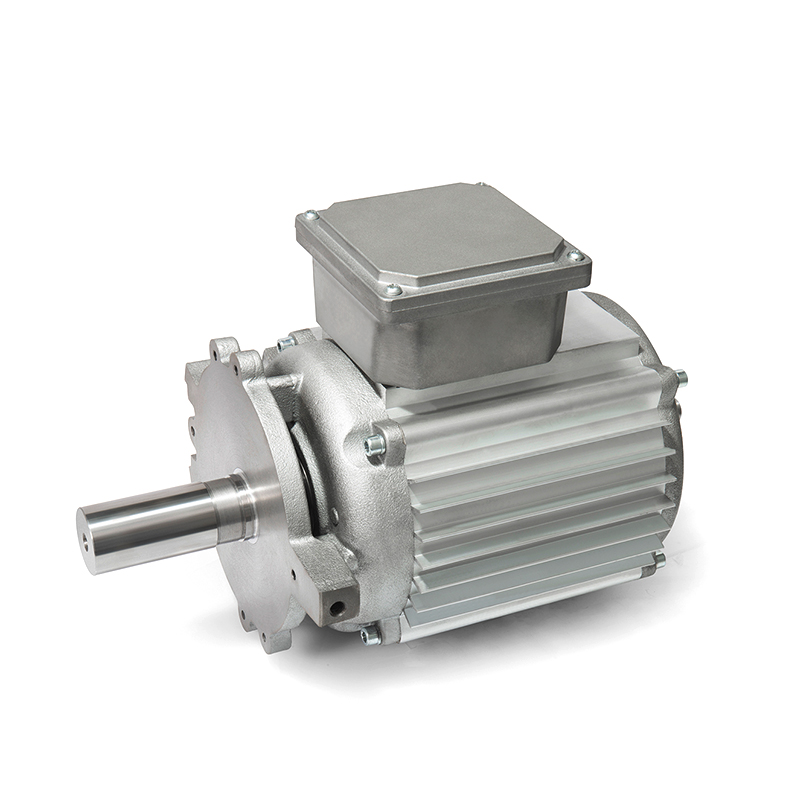
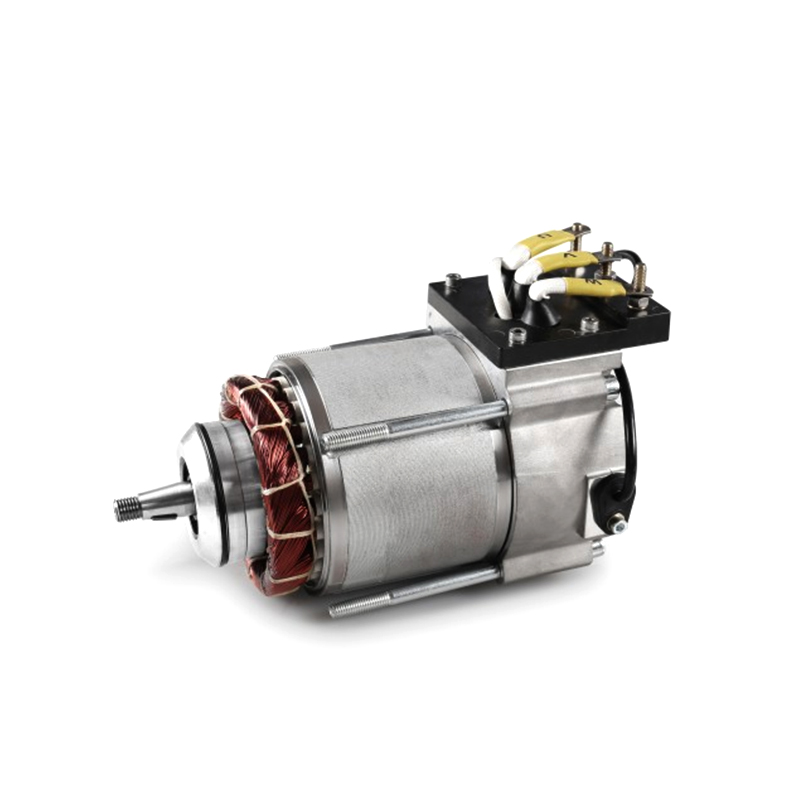
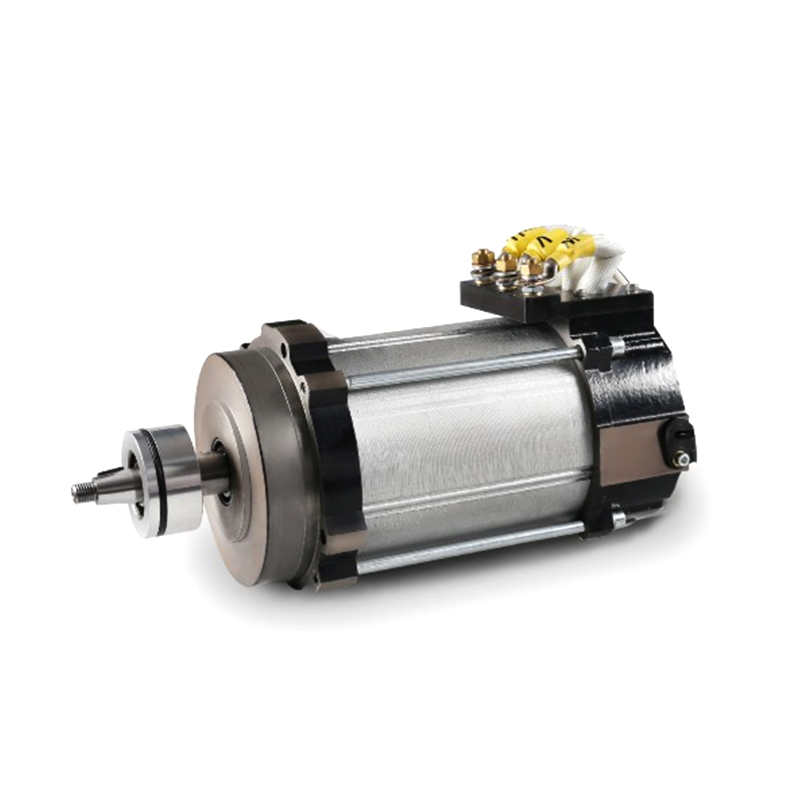
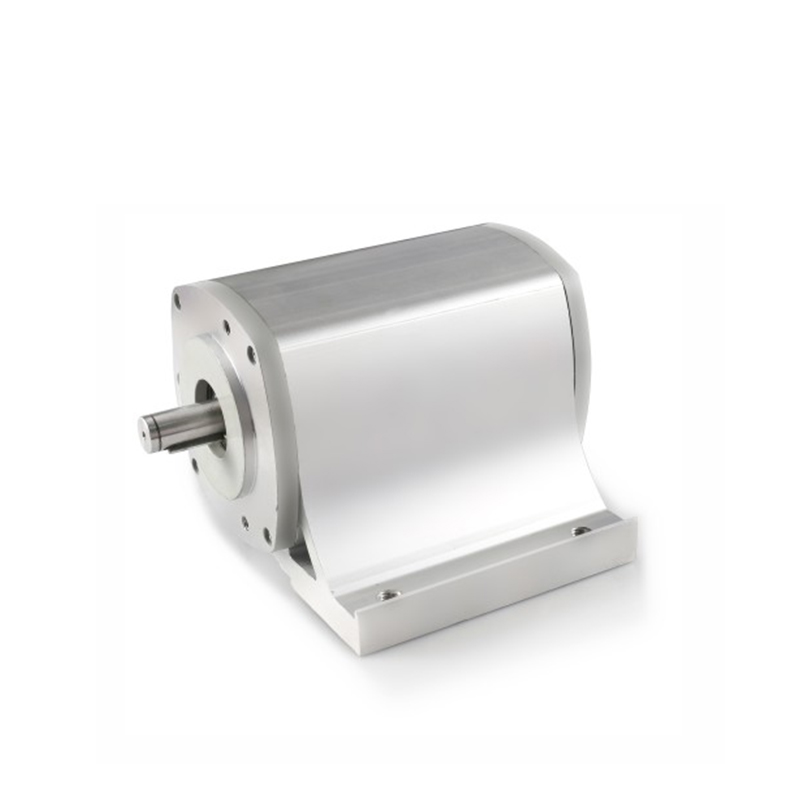
Brushless DC Motor (BLDC): The core of the system is the brushless DC motor. It consists of a stator (stationary part) with coils and a rotor (rotating part) with permanent magnets. The stator coils are energized sequentially to create a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor, producing rotational motion.
Reducer (Gearbox): The reducer is a mechanical device that reduces the speed of the motor while increasing torque. It consists of gears, such as spur gears, planetary gears, or helical gears, arranged in a specific configuration to achieve the desired speed reduction and torque multiplication. The reducer helps match the motor's speed to the application's requirements and provides mechanical advantage.
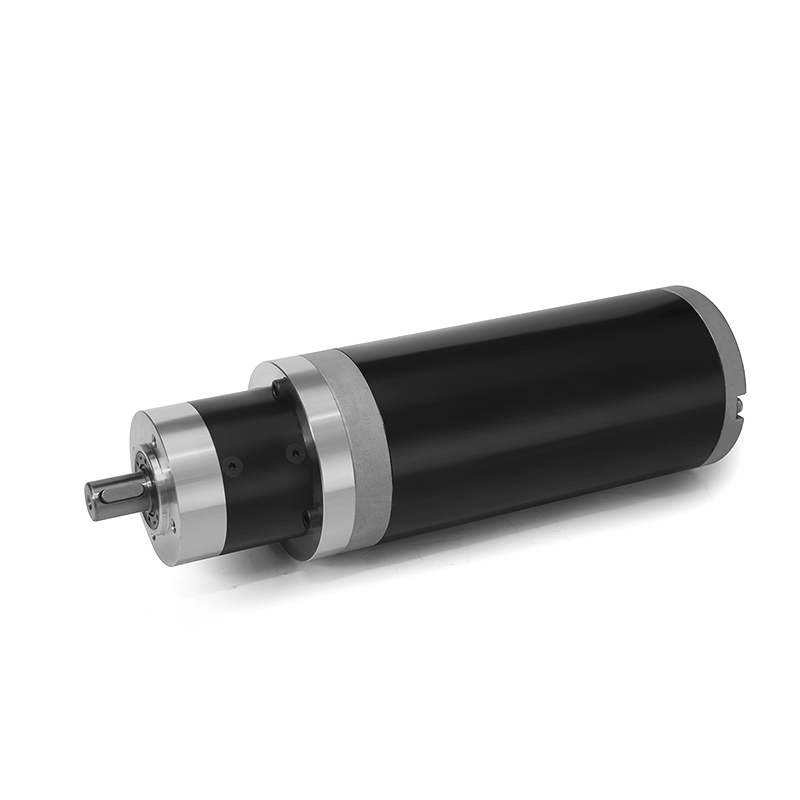

Encoder or Hall Effect Sensors: To control the motor's speed, position, and direction accurately, feedback devices like encoders or Hall effect sensors are often used. Encoders provide precise position feedback by generating pulses as the motor rotates, while Hall effect sensors detect the rotor's position based on the magnetic field. This feedback information is crucial for closed-loop control of the motor.
Motor Controller (Drive): The motor controller, also known as the motor drive or electronic speed controller (ESC), is responsible for regulating the power supplied to the motor based on input signals and feedback from sensors. It controls the timing and amplitude of current pulses sent to the motor coils, ensuring smooth operation, precise speed control, and protection against overcurrent or overheating.
Power Supply: A power supply unit provides the necessary electrical power to the motor controller and motor system. It converts AC mains power or DC voltage from batteries into the appropriate voltage and current levels required by the motor and controller.
Communication Interface: Many modern brushless geared motors come with communication interfaces such as UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter), SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), or CAN (Controller Area Network). These interfaces allow for external control, monitoring, and data exchange with other devices or systems, enhancing integration and functionality.
Working Together:
The motor controller receives input signals, typically from a microcontroller or a control system, specifying the desired speed, direction, and operating parameters.
Based on the input signals and feedback from sensors (encoders or Hall effect sensors), the motor controller calculates the appropriate timing and amplitude of current pulses to be sent to the motor coils.
The motor controller energizes the stator coils in a sequence determined by the motor's rotor position, creating a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor.
The reducer reduces the rotational speed of the motor while increasing torque, matching the motor's output to the load requirements of the application.
The combined action of the motor, reducer, feedback devices, and controller results in precise and efficient mechanical motion, allowing the brushless geared motor system to perform tasks such as driving conveyor belts, robotics, automated machinery, and more.
Brushless DC Motor (BLDC): The core of the system is the brushless DC motor. It consists of a stator (stationary part) with coils and a rotor (rotating part) with permanent magnets. The stator coils are energized sequentially to create a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor, producing rotational motion.
Reducer (Gearbox): The reducer is a mechanical device that reduces the speed of the motor while increasing torque. It consists of gears, such as spur gears, planetary gears, or helical gears, arranged in a specific configuration to achieve the desired speed reduction and torque multiplication. The reducer helps match the motor's speed to the application's requirements and provides mechanical advantage.

Encoder or Hall Effect Sensors: To control the motor's speed, position, and direction accurately, feedback devices like encoders or Hall effect sensors are often used. Encoders provide precise position feedback by generating pulses as the motor rotates, while Hall effect sensors detect the rotor's position based on the magnetic field. This feedback information is crucial for closed-loop control of the motor.
Motor Controller (Drive): The motor controller, also known as the motor drive or electronic speed controller (ESC), is responsible for regulating the power supplied to the motor based on input signals and feedback from sensors. It controls the timing and amplitude of current pulses sent to the motor coils, ensuring smooth operation, precise speed control, and protection against overcurrent or overheating.
Power Supply: A power supply unit provides the necessary electrical power to the motor controller and motor system. It converts AC mains power or DC voltage from batteries into the appropriate voltage and current levels required by the motor and controller.
Communication Interface: Many modern brushless geared motors come with communication interfaces such as UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter), SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), or CAN (Controller Area Network). These interfaces allow for external control, monitoring, and data exchange with other devices or systems, enhancing integration and functionality.
Working Together:
The motor controller receives input signals, typically from a microcontroller or a control system, specifying the desired speed, direction, and operating parameters.
Based on the input signals and feedback from sensors (encoders or Hall effect sensors), the motor controller calculates the appropriate timing and amplitude of current pulses to be sent to the motor coils.
The motor controller energizes the stator coils in a sequence determined by the motor's rotor position, creating a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor.
The reducer reduces the rotational speed of the motor while increasing torque, matching the motor's output to the load requirements of the application.
The combined action of the motor, reducer, feedback devices, and controller results in precise and efficient mechanical motion, allowing the brushless geared motor system to perform tasks such as driving conveyor belts, robotics, automated machinery, and more.
-
Feedback
Hotline:0086-15869193920
Time:0:00 - 24:00


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch italiano
italiano 中文简体
中文简体