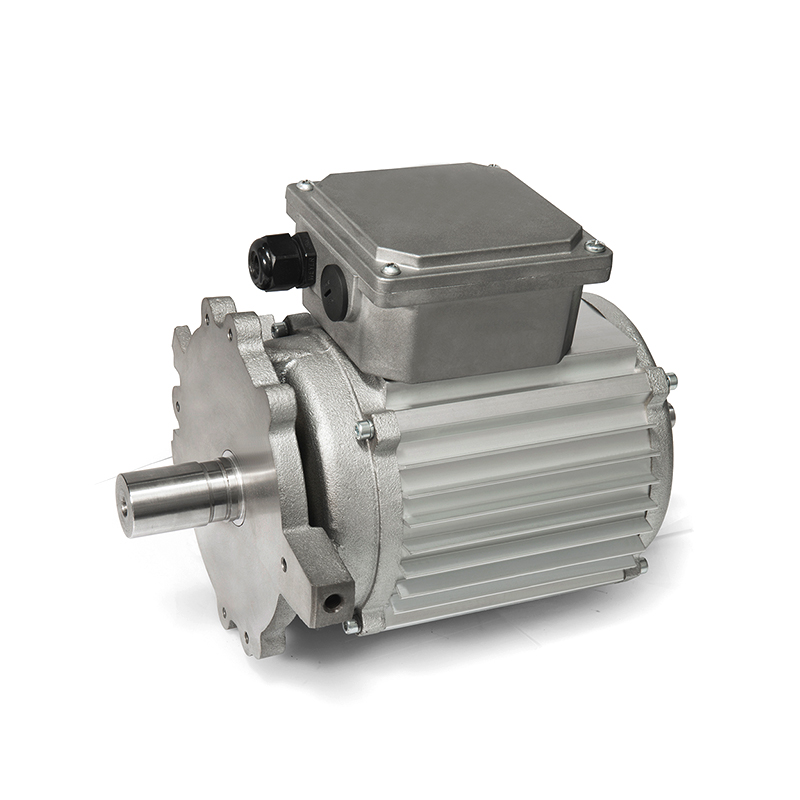
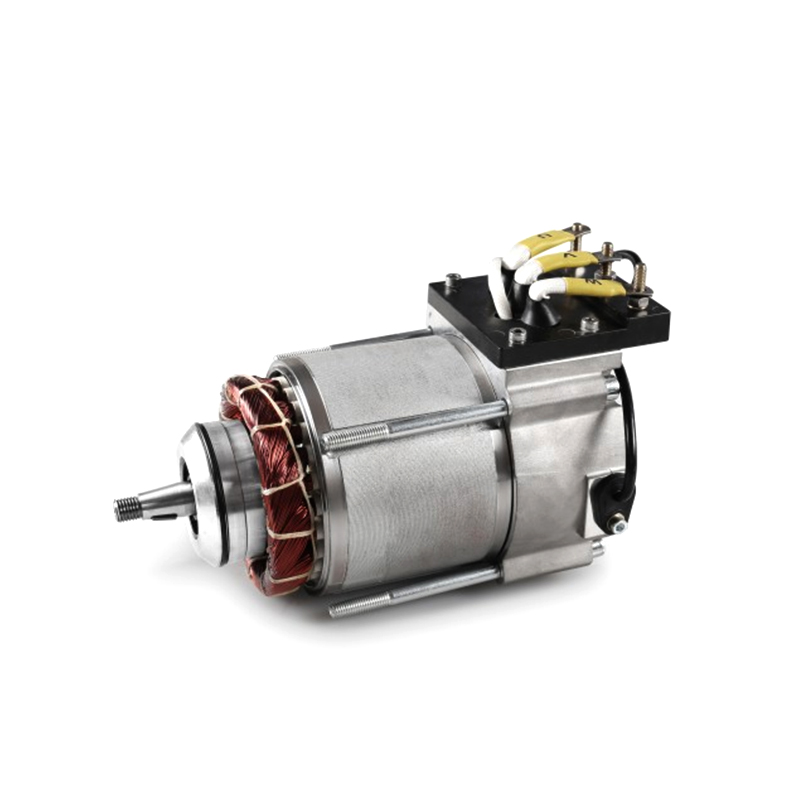
Author: Admin Date: 2024-03-27
What control and communication options are available for brushless geared motors, and how can they be integrated into automation systems?
In the realm of automation and motorized systems, brushless geared motors stand out as versatile solutions offering high efficiency, precise control, and seamless integration. A key aspect of harnessing the full potential of these motors lies in understanding the range of control and communication options available and how they can be effectively integrated into automation systems.
Brushless geared motors can be controlled using various methods, each offering unique advantages and suitability for different applications:
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Control: PWM control is a widely employed technique where the motor controller receives PWM signals to regulate the motor's speed and direction. By adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal, which represents the proportion of time the signal is high versus low, precise speed control can be achieved. This method is straightforward and effective for many automation tasks.
Analog Voltage Control: Some motor controllers accept analog voltage signals for speed control. By varying the voltage level within a specified range (e.g., 0-10V), the motor's speed can be adjusted accordingly. Analog control provides simplicity and compatibility with systems that output analog signals.
Digital Communication Protocols: Brushless geared motors equipped with digital communication interfaces offer advanced control capabilities. Common protocols include UART, SPI, I2C, and CAN, enabling bidirectional communication between the motor controller and external devices or systems. These protocols facilitate precise control, real-time monitoring, and data exchange, making them ideal for complex automation scenarios.

Fieldbus Protocols: In industrial automation, fieldbus protocols such as Profibus, Modbus, EtherCAT, and DeviceNet are prevalent for seamless integration of motor control into larger automation networks. These protocols standardize communication and enable efficient data exchange between components within the system.
Ethernet and TCP/IP: For networked automation environments, brushless motor controllers with Ethernet connectivity and support for TCP/IP protocols offer remote control, monitoring, and data sharing capabilities over Ethernet networks. This enables centralized control and data management in distributed automation setups.
Integrating brushless geared motors into automation systems involves several steps to ensure seamless operation and optimal performance:
Protocol Compatibility: Identify the communication protocol(s) supported by the motor controller and ensure compatibility with the automation system's communication interfaces. This may require configuring the control software or PLC program to generate compatible control signals.
Hardware Setup: Establish the physical connection between the motor controller and the automation system using appropriate cables, connectors, and network infrastructure. Ensure proper grounding and shielding to minimize electromagnetic interference.
Software Configuration: Develop or configure the control software to send control commands, receive feedback signals, and implement logic for motor control algorithms. Calibration and tuning may be necessary to optimize performance and responsiveness.
Feedback Mechanisms: Utilize feedback devices such as encoders or Hall effect sensors to provide accurate position, speed, and direction feedback to the motor controller. This enables closed-loop control and enhances precision in motion control applications.
Brushless geared motors can be controlled using various methods, each offering unique advantages and suitability for different applications:
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Control: PWM control is a widely employed technique where the motor controller receives PWM signals to regulate the motor's speed and direction. By adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal, which represents the proportion of time the signal is high versus low, precise speed control can be achieved. This method is straightforward and effective for many automation tasks.
Analog Voltage Control: Some motor controllers accept analog voltage signals for speed control. By varying the voltage level within a specified range (e.g., 0-10V), the motor's speed can be adjusted accordingly. Analog control provides simplicity and compatibility with systems that output analog signals.
Digital Communication Protocols: Brushless geared motors equipped with digital communication interfaces offer advanced control capabilities. Common protocols include UART, SPI, I2C, and CAN, enabling bidirectional communication between the motor controller and external devices or systems. These protocols facilitate precise control, real-time monitoring, and data exchange, making them ideal for complex automation scenarios.

Fieldbus Protocols: In industrial automation, fieldbus protocols such as Profibus, Modbus, EtherCAT, and DeviceNet are prevalent for seamless integration of motor control into larger automation networks. These protocols standardize communication and enable efficient data exchange between components within the system.
Ethernet and TCP/IP: For networked automation environments, brushless motor controllers with Ethernet connectivity and support for TCP/IP protocols offer remote control, monitoring, and data sharing capabilities over Ethernet networks. This enables centralized control and data management in distributed automation setups.
Integrating brushless geared motors into automation systems involves several steps to ensure seamless operation and optimal performance:
Protocol Compatibility: Identify the communication protocol(s) supported by the motor controller and ensure compatibility with the automation system's communication interfaces. This may require configuring the control software or PLC program to generate compatible control signals.
Hardware Setup: Establish the physical connection between the motor controller and the automation system using appropriate cables, connectors, and network infrastructure. Ensure proper grounding and shielding to minimize electromagnetic interference.
Software Configuration: Develop or configure the control software to send control commands, receive feedback signals, and implement logic for motor control algorithms. Calibration and tuning may be necessary to optimize performance and responsiveness.
Feedback Mechanisms: Utilize feedback devices such as encoders or Hall effect sensors to provide accurate position, speed, and direction feedback to the motor controller. This enables closed-loop control and enhances precision in motion control applications.
-
Feedback
Hotline:0086-15869193920
Time:0:00 - 24:00


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch italiano
italiano 中文简体
中文简体