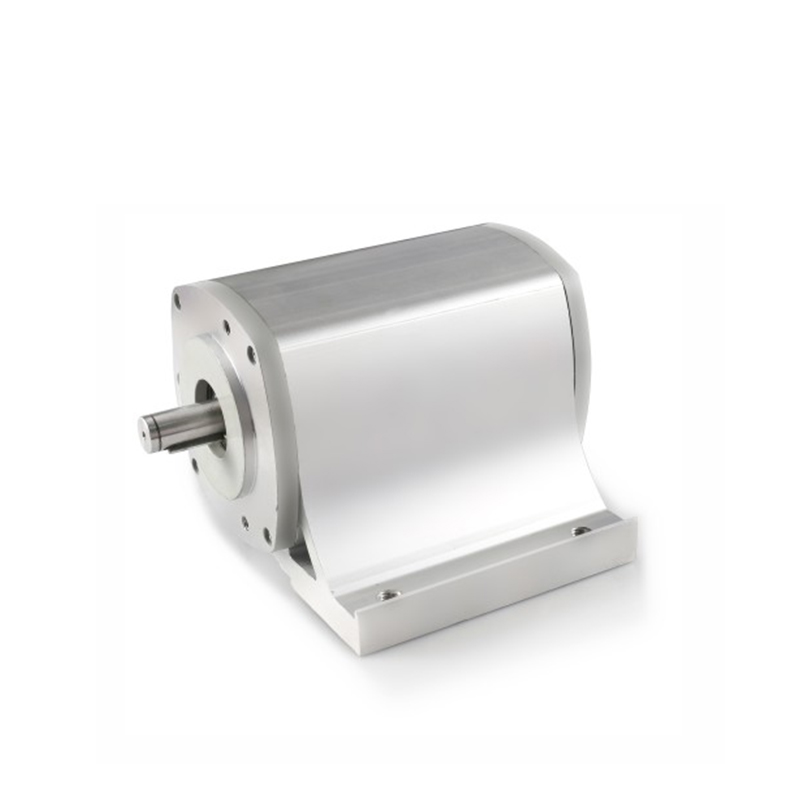
Need Precise Power and Control? How DC Geared Motors Drive Modern Automation
In the world of automation, robotics, and smart technology, motion is everything. But raw speed alone is often useless without the necessary force and precise control to make it effective. How do engineers and designers transform the high-speed, low-torque spin of a standard DC motor into the powerful, controlled, and actionable movement that powers everything from robotic arms to automatic window blinds? The answer lies in a fundamental component of motion control: the DC Geared Motor. This integrated system is the workhorse behind countless applications, delivering the perfect balance of speed and force. But what exactly is it, and how can you leverage its power for your next project?
The Best of Both Worlds: What is a DC Geared Motor?
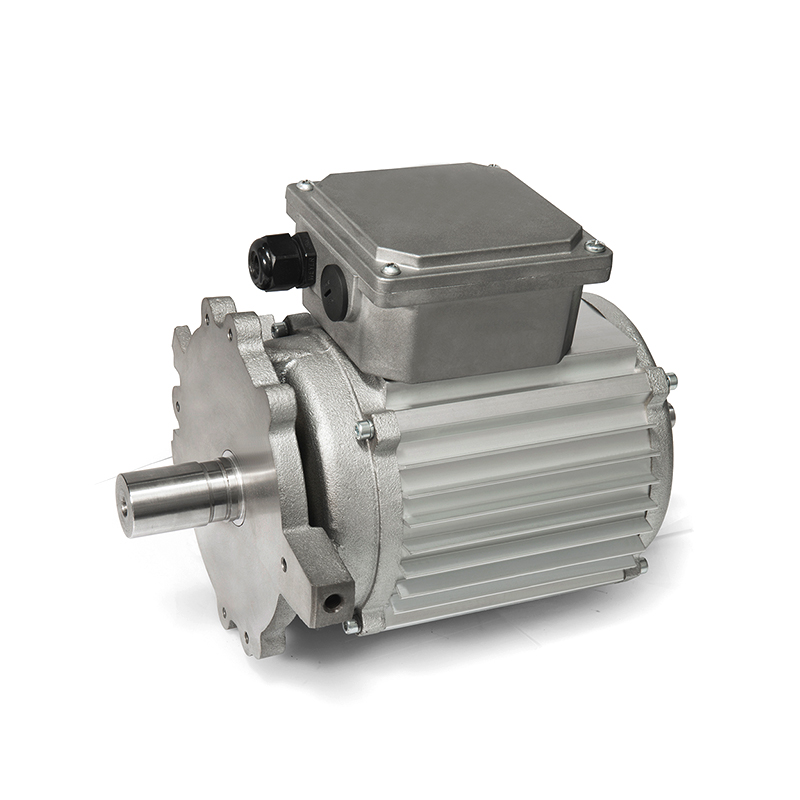
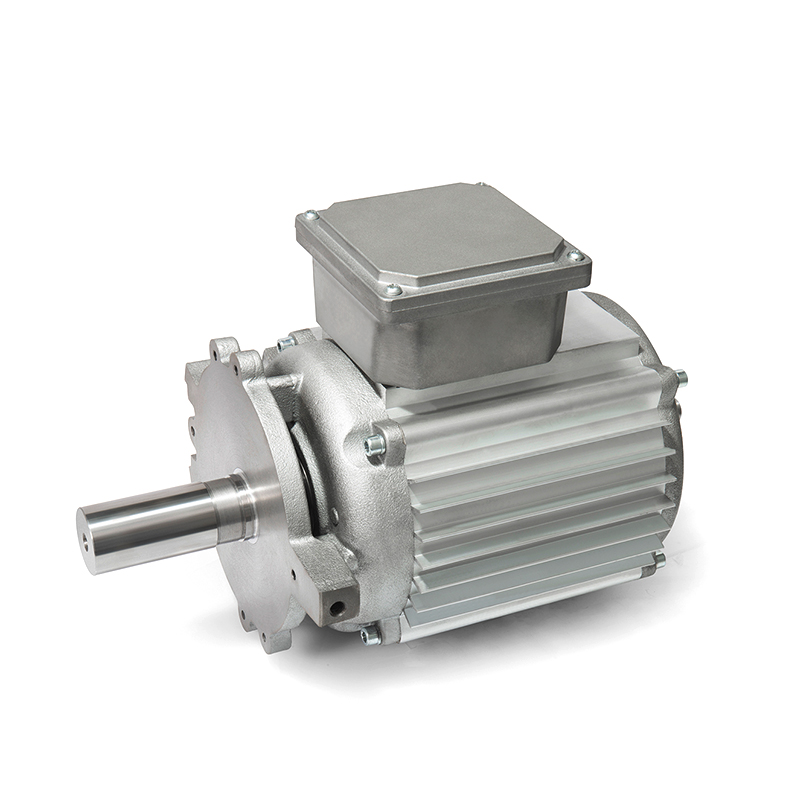
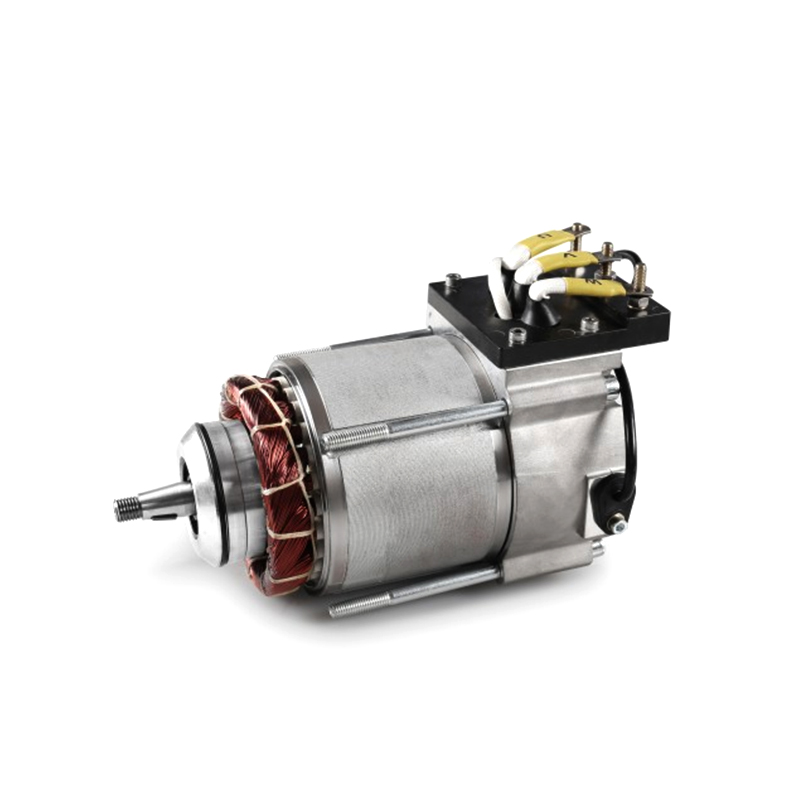
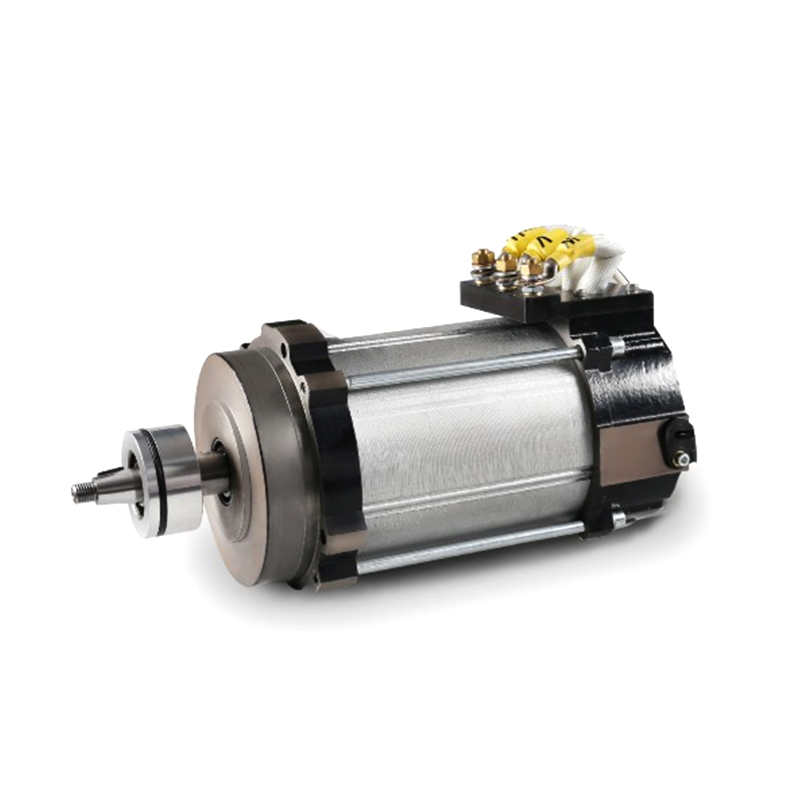
A DC Geared Motor is not a single component but a sophisticated system that integrates two key elements: a standard DC motor and a gear reduction assembly, often called a gearhead or gearbox. The DC motor provides the initial rotational force (RPM), while the gearbox acts as a torque multiplier and speed reducer. Through a series of internal gears, the gearhead trades the motor’s high rotational speed for a proportional increase in output torque (rotational force). The result is a compact, self-contained unit that delivers lower output speed but significantly higher usable force, making it ideal for applications that need to push, pull, lift, or drive a load.
Why Integration is Key: The Unbeatable Advantages
Choosing a pre-engineered DC Geared Motor offers far more benefits than simply pairing a separate motor and gearbox. The integrated design provides critical advantages:
- High Torque at Low Speeds: This is the primary purpose. The gear reduction allows small, energy-efficient motors to produce impressive amounts of torque, enabling them to move heavy loads that would stall a standard DC motor instantly.
- Compact and Space-Efficient Design: Manufacturers design these units to be incredibly space-conscious. The motor and gearbox are housed together, creating a streamlined package that simplifies installation in tight spaces where a custom assembly wouldn’t fit.
- Improved Precision and Control: The reduced speed allows for more precise positional control. This is essential for applications like robotics, where accurate movement is more critical than raw speed. It also makes the motor easier to manage with electronic speed controllers.
- Enhanced Durability and Reliability: As a pre-matched and assembled unit, the motor and gearhead are engineered to work in perfect harmony. This reduces misalignment issues, minimizes wear on components, and extends the overall lifespan of the system.
- Simplified Sourcing and Assembly: Instead of sourcing, sizing, and mounting two separate components, you select a single integrated unit. This drastically reduces design time, complexity, and the potential for integration errors.
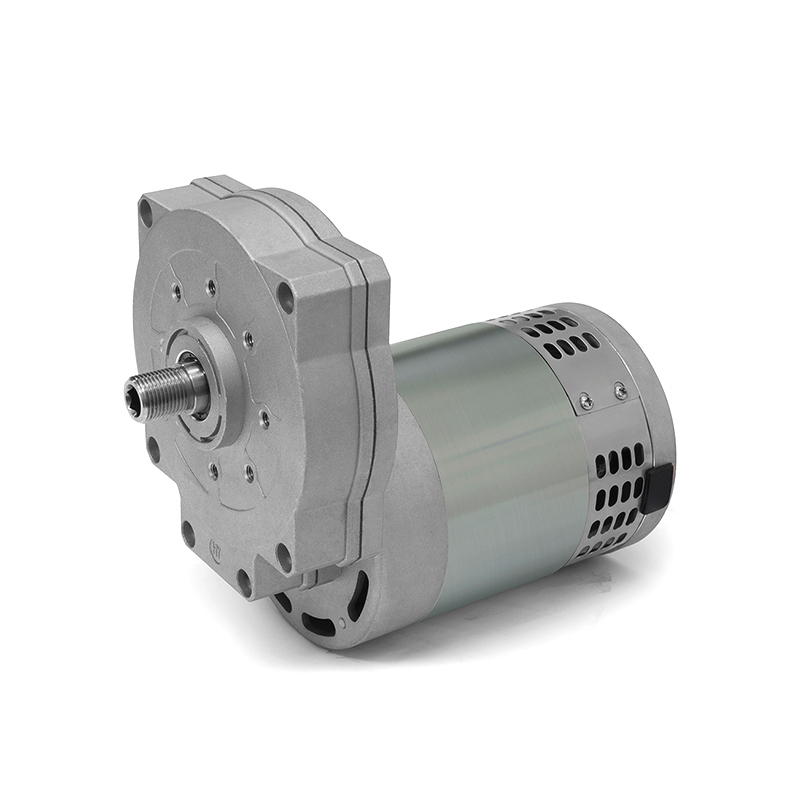

A World in Motion: Where Are DC Geared Motors Used?
The versatility of DC Geared Motors makes them indispensable across a stunning array of industries:
- Robotics and Automation: Powering joint movements in robotic arms, driving the wheels of mobile robots (AGVs), and controlling actuators in automated machinery.
- Automotive Applications: Operating power windows, adjusting seats, controlling windshield wipers, and activating power locks.
- Medical Equipment: Driving pumps in infusion devices, adjusting hospital beds and patient chairs, and powering movement in diagnostic equipment.
- Consumer Electronics and Smart Home Devices: Raising and lowering projector screens, opening and closing automatic curtains, and operating smart locks and pet feeders.
- Industrial Machinery: Controlling valve actuators, driving conveyor belts at precise speeds, and powering material handling equipment.
- Vending Machines and Kiosks: Driving product spirals and dispensing mechanisms reliably.
Selecting the Right Motor for Your Application: Key Specifications
To harness the full potential of a DC Geared Motor, you must match it to your application’s requirements. Focus on these critical specs:
- Rated Voltage: The operating voltage (e.g., 12V or 24V DC) which determines the motor’s speed and torque characteristics.
- Output Speed: The final speed at the gearbox’s output shaft, measured in RPM. This is determined by the motor’s base speed and the gear ratio.
- Output Torque: The amount of rotational force the motor can exert, usually measured in kg-cm or oz-in. This must exceed the requirement of your load.
- Gear Ratio: The ratio of input speed to output speed (e.g., 50:1). A higher ratio means more torque but less output speed.
- Duty Cycle: Ensure the motor is rated for your application’s required run time (continuous vs. intermittent duty).
Power Your Innovation with Precision
The DC Geared Motor is a testament to elegant engineering—a simple concept that unlocks a universe of motion possibilities. It is the essential link between electronic control and physical action, providing the muscle and control that modern automated systems demand.
-
Feedback
Hotline:0086-15869193920
Time:0:00 - 24:00


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch italiano
italiano 中文简体
中文简体